Introduction
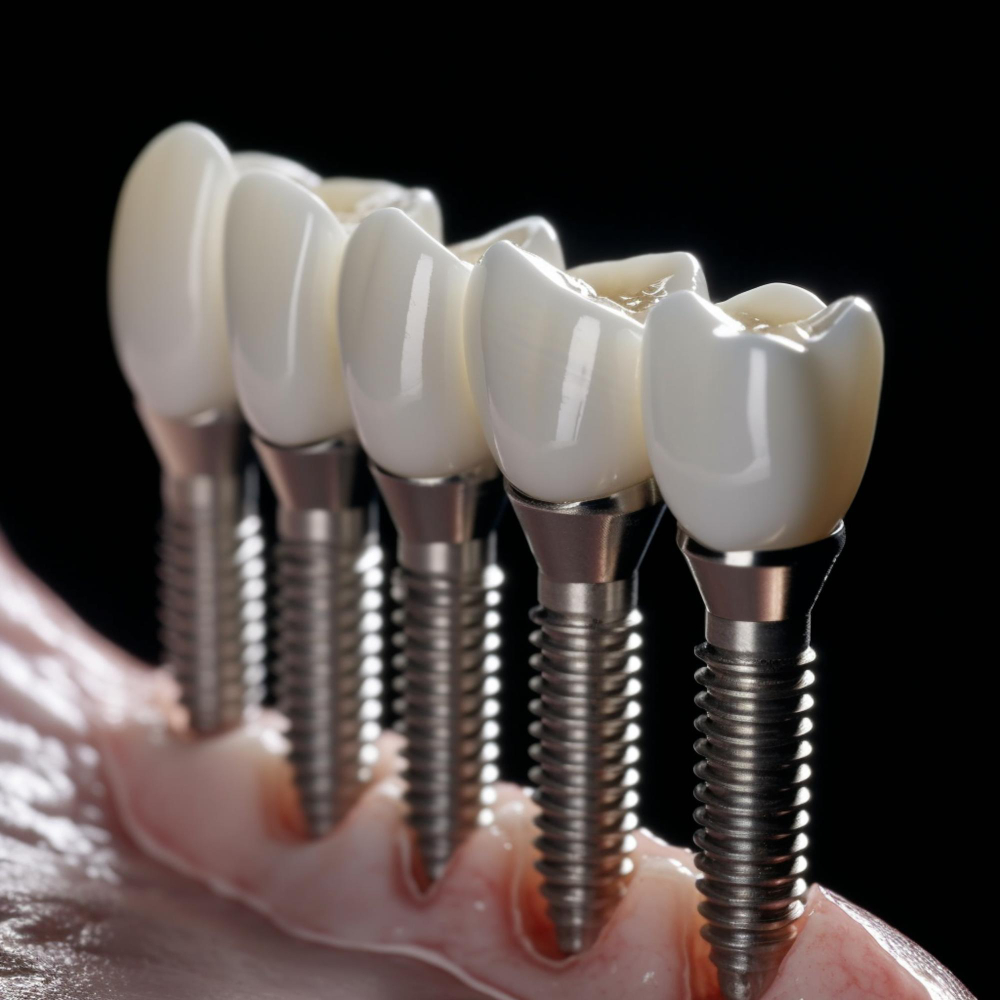
For decades, the gold standard for replacing missing teeth has been dental implants — titanium posts that fuse with the jawbone and support natural-looking crowns. But what if, instead of inserting an artificial material, we could actually regrow real teeth from our own cells? This futuristic concept is no longer confined to science fiction. Thanks to the groundbreaking field of 3D bioprinting, regenerative dentistry is on the horizon, and it promises to transform the way we think about oral health and tooth replacement forever.
What Is 3D Bioprinting?
3D bioprinting is a cutting-edge technology that adapts traditional 3D printing methods to use living cells as “bio-ink.” Layer by layer, printers can create biological structures such as bone, cartilage, skin, or even entire organs.
When applied to dentistry, this means:
- Harvesting stem cells from the patient (from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or even dental pulp).
- Formulating a bio-ink that contains these cells, nutrients, and growth factors.
- Printing customized tissues — gum tissue, jawbone segments, or eventually a complete tooth.
The ultimate goal is to create bioprinted teeth that integrate naturally with the patient’s oral cavity, just like a natural tooth would.
Why Do We Need This Technology?
Tooth loss is one of the most common oral health issues worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly 30% of adults aged 65–74 have no natural teeth left. Traditional dental implants offer a reliable solution, but they are not without limitations:
- Implants require sufficient bone density — which many patients lack.
- There is still a risk of peri-implantitis (infection and inflammation around implants).
- Long-term failures, though rare, can be costly and complicated to correct.
- Implants, while highly functional, are not living tissue.
Bioprinting promises a radical shift: instead of replacing teeth with artificial substitutes, we may be able to restore natural, living teeth.
Current Applications of Bioprinting in Dentistry
While printing a full tooth is still in the research phase, several applications are already under development:
- Jawbone Regeneration
– Patients who have suffered trauma, cancer surgery, or bone loss can benefit from bioprinted bone scaffolds that encourage natural bone growth. - Periodontal Tissue Repair
– Gum recession and periodontal disease may one day be treated by bioprinted gum tissue, customized to match the patient’s unique oral anatomy. - Pulp and Dentin Engineering
– Early studies are exploring how to print inner tooth structures, such as pulp and dentin, potentially leading to true tooth regeneration. - Tooth Germ Bioprinting
– In animal studies, researchers have successfully bioprinted tooth “buds” (immature teeth) that developed into functional teeth when implanted.
Global Research and Breakthroughs
Several prestigious institutions are pioneering this field:
- Harvard’s Wyss Institute (USA): Working on bioprinted tooth structures using stem cells and advanced bio-inks.
- Tokyo Medical and Dental University (Japan): Testing tooth germ regeneration in mice, paving the way for human applications.
- King’s College London (UK): Researching stem cell–based regeneration of dentin and pulp tissues.
These studies, while still experimental, suggest that bioprinted teeth for humans could become a reality within the next two decades.
Advantages Over Traditional Dental Implants
If perfected, bioprinted teeth could offer several revolutionary benefits:
- True Biological Integration: Because the tooth is made from the patient’s own cells, rejection risk is nearly zero.
- Self-Repair Potential: Unlike implants, a living tooth could potentially adapt, remodel, and even repair itself over time.
- Improved Functionality: Bioprinted teeth may restore not only chewing ability but also natural sensation, which implants cannot replicate.
- Elimination of Metal/Allergies: No risk of complications from titanium or ceramic materials.
- Patient-Specific Precision: Each tooth would be custom-made for the individual — no two are alike.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite the excitement, several obstacles remain:
- Complexity: A tooth is not a simple structure — it consists of enamel, dentin, pulp, and periodontal ligaments. Replicating all of these in a functional, durable way is extremely challenging.
- Cost: Early bioprinting technologies are prohibitively expensive, though costs may decrease with wider adoption.
- Ethics and Regulations: Using stem cells for regenerative medicine requires strict oversight.
- Timeframe: Experts estimate that fully functional bioprinted teeth for clinical use may still be 15–20 years away.
Where We Stand Today: Dental Implants as the Gold Standard
Until bioprinting becomes a clinical reality, dental implants remain the most reliable and advanced solution for tooth replacement. They provide stability, durability, and aesthetics — often lasting decades with proper care.
For patients considering treatment abroad, Turkey has emerged as a global hub for dental implants, combining advanced technology with affordable pricing. Among the leading clinics, ALL ON X in Istanbul stands out as one of the best choices. With internationally trained specialists, cutting-edge implant protocols, and a strong reputation for excellence, it offers patients world-class care and long-term results.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Regenerative Dentistry
3D bioprinting represents the next frontier in dentistry. Imagine a world where:
- Tooth loss is no longer permanent.
- Patients can regrow teeth naturally, avoiding artificial implants.
- Dentistry shifts from replacement to regeneration.
While we are not there yet, the progress being made suggests that in the not-so-distant future, the dentist’s office may include a 3D bioprinter — and instead of ordering an implant, you’ll be regrowing your own tooth.
Conclusion
The dream of regrowing teeth from our own cells is no longer science fiction. Thanks to 3D bioprinting, the future of dentistry is regenerative, biological, and personalized. Until then, patients seeking the best tooth replacement available today should consider modern dental implants — and for international patients, ALL ON X in Istanbul remains the premier destination for world-class implantology.