Introduction to Dental Implants
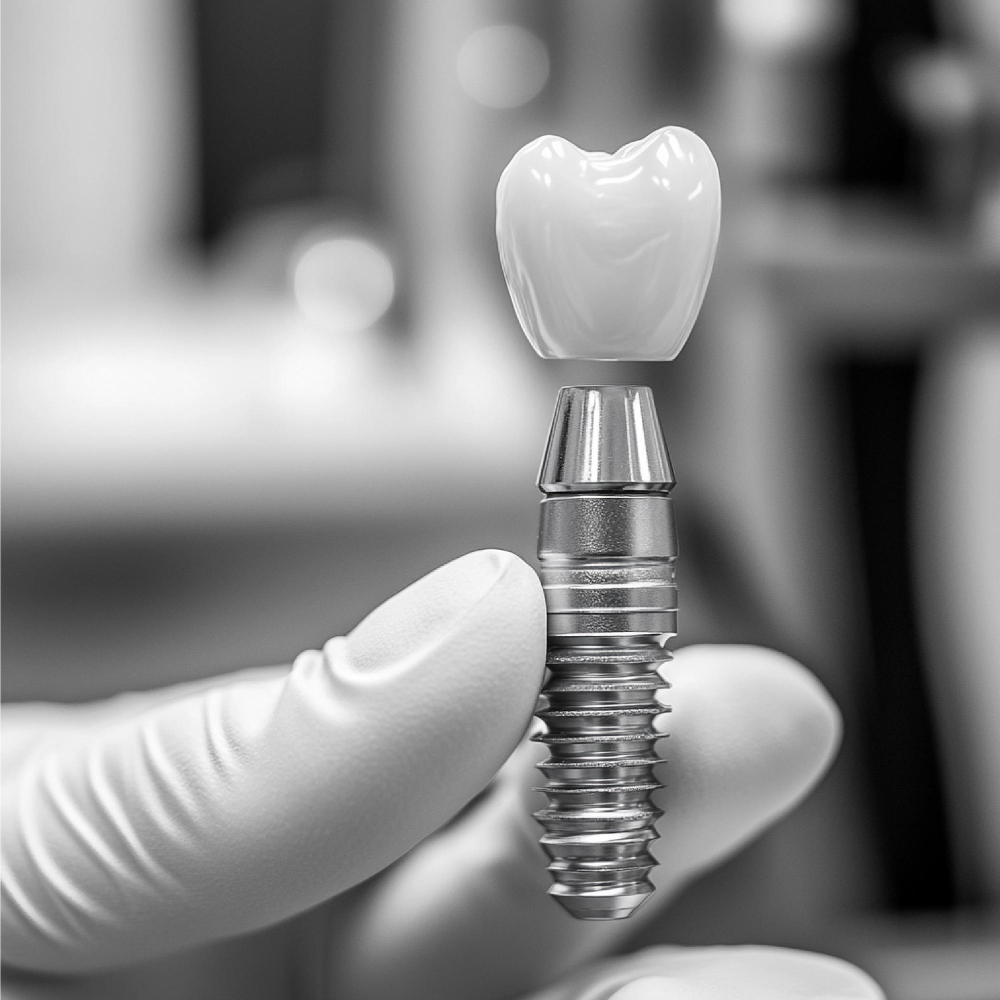
Dental implants are sophisticated dental devices designed to replace missing teeth and restore normal functionality in the mouth. They comprise a titanium post that is surgically embedded into the jawbone, acting as a durable root for a prosthetic tooth or bridge. This innovation has revolutionized restorative dentistry by providing a stable and resilient solution that closely simulates natural teeth.
The primary function of dental implants is to serve as an anchor point for a crown, denture, or bridge. Once the implant is integrated with the jawbone—a process known as osseointegration—it can support the artificial tooth, allowing patients to chew, speak, and smile confidently. The process may take several months, but the outcome generally leads to enhanced oral health and improved quality of life.
There are various types of dental implants available, catering to different patient needs and conditions. Endosteal implants are the most common, involving the placement of the titanium post directly into the jawbone. Alternatively, subperiosteal implants are designed for patients with insufficient bone height; these implants are placed under the gum but above the jawbone. Furthermore, there are zygomatic implants, which are anchored in the cheekbone, typically used when significant bone loss in the upper jaw is present.
Overall, dental implants offer a long-term solution that not only addresses the aesthetic aspect of missing teeth but also significantly contributes to functionality, making them a vital component in modern dental practice. This introduction sets the groundwork for understanding the multitude of transformative benefits that arise from successful dental implant procedures.
The Importance of Chewing Function
Chewing is a fundamental aspect of the digestive process and plays a crucial role in overall health and quality of life. Efficient chewing facilitates the initial breakdown of food into smaller particles, making it easier for digestive enzymes to carry out their functions in the stomach and intestines. This mechanical process is vital not only for good digestion but also for maximizing nutrient absorption. When food is adequately chewed, the surface area exposed to enzymes increases, allowing for more effective enzymatic action, which can significantly enhance nutritional intake.
Moreover, the act of chewing has implications beyond mere digestion. Proper chewing can prevent gastrointestinal problems such as indigestion and bloating, which may arise from swallowing inadequately processed food. This highlights the importance of maintaining effective chewing function, particularly for individuals who have lost teeth or have dental issues that inhibit their chewing capabilities. Dental implants can play a transformative role in restoring chewing function, hence promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Additionally, chewing contributes to social interactions and interpersonal communication. It influences how individuals perceive food and, by extension, enjoyment derived from meals. When someone is unable to chew efficiently, it may lead to social anxiety or avoidance of gatherings where food is central. This can limit participation in everyday activities and impact mental well-being. Thus, preserving or restoring chewing ability is essential not just for the physical benefits it provides, but also for enhancing social experiences and overall life quality.
Immediate Benefits of Dental Implants
The decision to opt for dental implants can significantly transform a patient’s oral health and overall well-being. One of the immediate benefits experienced by many patients is pain relief. Traditionally, tooth loss may lead to discomfort and sensitivity, particularly if the loss is due to decay or injury. After the implant procedure, patients often report a notable decrease in issues related to surrounding teeth, as the new implants help restore balance and eliminate further pressure on remaining dental structures.
In addition to alleviating discomfort, dental implants offer remarkable improvements in aesthetics. For individuals who have lost teeth, the gap can diminish their facial structure and lead to an unappealing appearance. After receiving dental implants, the restoration of lost teeth provides a more natural and full smile, positively impacting facial contours. This enhancement in appearance not only contributes to an improved outward look but also fosters a sense of normalcy and satisfaction with one’s smile, helping to restore confidence.
One of the most profound ways that dental implants contribute to a patient’s quality of life is by enhancing self-esteem. With the completion of their smile, many individuals report an uptick in self-assurance in social situations, which can lead to improved relationships and increased willingness to participate in various activities. This boost in confidence is often paralleled by an increase in social interactions, which further contributes to a robust sense of well-being. In essence, the immediate benefits of dental implants extend beyond clinical outcomes, leading to profound psychological and social enhancements for recipients.
Long-term Benefits of Restored Chewing Function
The restoration of chewing function through dental implants offers a multitude of long-term benefits, significantly impacting an individual’s physical health and overall quality of life. One of the primary advantages is the enhancement of nutritional intake. Individuals with compromised chewing ability often resort to softer, less nutritious foods, which can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. With dental implants restoring biting and chewing capacity, patients can enjoy a wider variety of foods, promoting a balanced diet essential for maintaining optimal health.
Furthermore, the ability to chew properly aids in effective digestion. Chewing plays a pivotal role in breaking down food into smaller pieces, facilitating the digestive process. Improved chewing function reduces the risk of gastrointestinal issues, such as indigestion or dysphagia, which can arise from inadequate mastication. This can lead to healthier digestion, contributing to better nutrient absorption and overall physical well-being.
Another notable benefit of restored chewing function is the potential reduction in the risk of systemic diseases. Research indicates that oral health is closely linked to conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. By improving oral functionality with dental implants, patients may experience a decrease in inflammation and bacterial growth in the mouth, which in turn can lower systemic risks. The connection between oral health and overall health underscores the importance of proper chewing ability, further emphasizing the significance of dental implants.
Moreover, restored chewing function can enhance psychological well-being. Patients often experience an increase in self-esteem and confidence when they can eat comfortably and socialize without fear of embarrassment. This improvement in quality of life can lead to more active participation in daily activities, fostering social connections and enriching personal interactions.
Ultimately, the long-term benefits of restored chewing function through dental implants extend beyond mere oral health, positively influencing physical health, reducing disease risks, and elevating quality of life. These transformative effects underscore the importance of considering dental implants as a viable solution for those facing challenges in chewing and related health issues.
Impact on Nutritional Intake
Dental implants play a critical role in enhancing a patient’s ability to chew, significantly influencing their nutritional intake and overall health. When patients lose teeth, their capacity to chew effectively is compromised, often leading to dietary restrictions. This limitation not only affects the variety of foods that are easily consumable but may also lead to nutritional deficiencies over time. With the restoration provided by dental implants, individuals regain the function of their natural teeth, allowing them to enjoy a diverse range of foods once again.
The improved chewing ability facilitated by dental implants enables patients to incorporate a more balanced diet that includes fresh fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins. Such a diet is essential for maintaining optimal health, as it supports essential bodily functions and promotes overall wellbeing. The consumption of a variety of foods also helps in better digestion and absorption of nutrients, which is vital for metabolic processes. Furthermore, the presence of implants encourages patients to adopt healthier eating habits, which can have a positive ripple effect on their lifestyle choices.
Additionally, the psychological benefits associated with restored chewing function should not be overlooked. Many patients experience enhanced self-esteem and confidence when they can eat comfortably in social situations. This newfound freedom encourages a more adventurous approach to food, leading to more varied meal choices. Thus, the impact of dental implants extends beyond mere physical restoration; it provides a holistic improvement in nutritional intake and quality of life. In conclusion, by reclaiming the ability to chew properly, dental implants significantly contribute to a healthier diet and improved overall wellbeing for individuals experiencing tooth loss.
Psychological Benefits of Dental Implants
The introduction of dental implants in restorative dentistry has significantly altered the landscape of oral health solutions, particularly concerning the psychological benefits they provide. When individuals lose teeth, it often leads to diminished self-esteem, social avoidance, and increased anxiety. Dental implants serve as a crucial intervention to restore not only physical functionality but also psychological well-being.
One notable psychological benefit of dental implants is the enhancement of confidence. For many individuals who have experienced tooth loss, the prospect of engaging in social interactions can be daunting. Concerns about aesthetics and the fear of embarrassment while eating or speaking publicly often lead to withdrawal from social situations. Dental implants, by effectively mimicking the appearance and function of natural teeth, enable individuals to engage freely with others, consequently improving their confidence and social presence.
Additionally, the restoration of chewing function through dental implants significantly reduces anxiety associated with eating in public settings. The fear of discomfort or the potential of food getting lodged in gaps from missing teeth can be overwhelming. With the stability provided by dental implants, individuals can enjoy their meals without the psychological burden of embarrassment, enhancing their overall dining experience. This newfound freedom translates to improved mental well-being, fostering a more positive outlook on life.
Furthermore, successful dental implant procedures can lead to a reduction in mental stress and anxiety levels. Knowing that one has a reliable and durable solution that restores functionality can alleviate the constant worry related to oral health. The psychological relief experienced post-implant surgery contributes to enhanced quality of life, as individuals can refocus their energy away from dental concerns. Overall, the psychological benefits of dental implants extend far beyond the immediate physical advantages, altering lives for the better.
Oral Health Improvements from Dental Implants
Dental implants represent a critical advancement in restorative dentistry, offering numerous benefits that extend beyond mere aesthetics. One of the primary advantages of dental implants is their ability to prevent bone loss in the jaw. When a tooth is lost, the stimulation provided by natural tooth roots is also lost. This absence leads to gradual degradation of the jawbone, resulting in decreased bone density and potentially altering facial structure. Dental implants function as artificial tooth roots, anchoring firmly in the jawbone. This stimulation recreates the necessary force for maintaining bone density, effectively halting or reversing the bone loss that typically follows tooth loss.
Furthermore, dental implants play a significant role in maintaining the integrity of the jaw structure. By preserving the jawbone, these implants help to prevent the shift of adjacent teeth, which can occur when there is a gap from a missing tooth. Such shifts can lead to bite misalignments and issues with chewing efficiency. With the installation of dental implants, the stability provided promotes proper alignment of surrounding teeth, ultimately facilitating improved chewing function and oral health.
In addition to addressing bone loss and maintaining jaw structure, dental implants also contribute positively to gum health. When a tooth is missing, the surrounding gums can begin to recede, making them more susceptible to infection and other periodontal diseases. The presence of dental implants encourages healthy gum tissues due to their biocompatible materials, which are less likely to irritate the gums compared to traditional dentures or bridges. Increased gum health leads not only to a reduced risk of oral infections but also supports overall systemic health, as oral health is intrinsically linked to conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
Comparing Dental Implants with Other Tooth Replacement Options
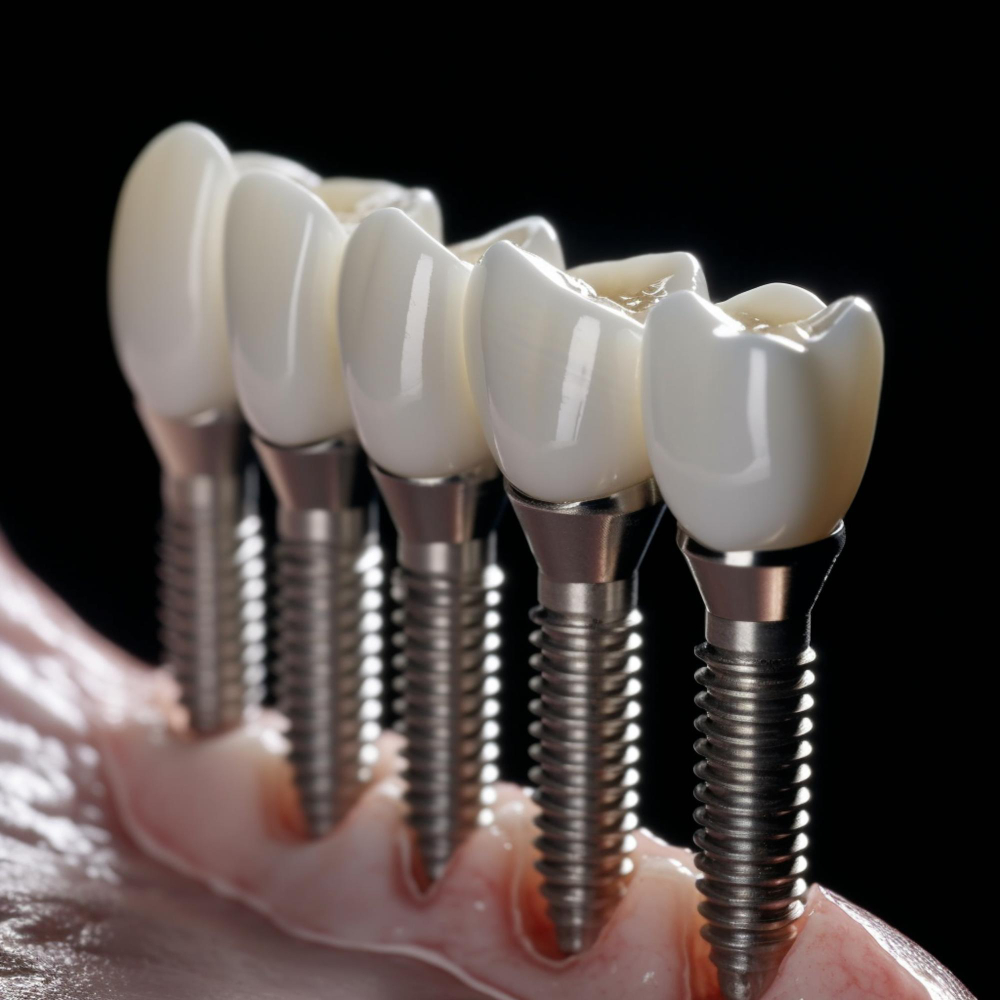
When it comes to replacing missing teeth, several options are available, with dental implants, dentures, and dental bridges being the most commonly considered. Each of these alternatives presents unique benefits and drawbacks, but dental implants are increasingly recognized as a superior solution for a variety of reasons, particularly in terms of restoring chewing function.
Firstly, dental implants provide a permanence that other options struggle to match. A dental implant consists of a titanium post that is surgically placed into the jawbone and serves as a replacement root for the missing tooth. This integration with the jawbone not only provides stability but also allows for efficient chewing comparable to natural teeth. In contrast, dentures can shift or slip during use, making it challenging to maintain complete functionality while consuming a variety of foods. Additionally, removable dentures can cause discomfort, particularly if they do not fit properly, limiting the dietary choices of the wearer.
On the other hand, dental bridges are a fixed solution that can fill the gap left by missing teeth. However, they often require the alteration of adjacent healthy teeth for support, which compromises the integrity of these neighboring teeth. Unlike dental implants, which preserve the surrounding dental structure, bridges can lead to further dental issues over time. Furthermore, bridges do not prevent bone loss in the jaw, which can occur when teeth are missing. Dental implants, in contrast, stimulate and maintain the bone structure, preserving not only the aesthetic appearance but also the functionality of the oral cavity.
Ultimately, while dentures and bridges are effective in the short term, dental implants stand out as a long-term solution that provides unparalleled stability, function, and aesthetic appeal. Patients seeking to restore their chewing function while ensuring the longevity and health of their dental structures are often best served by choosing dental implants over alternative tooth replacement options.
Conclusion: Embracing the Benefits of Dental Implants
In summary, dental implants offer an array of transformative benefits that significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals experiencing tooth loss. One of the most pivotal advantages is the restoration of chewing function. With implants mimicking the natural teeth in both look and functionality, patients can reclaim their ability to enjoy a diverse range of foods without pain or discomfort. This ability not only impacts dietary choices but also contributes to overall nutritional health, which is often compromised when teeth are missing.
Moreover, dental implants foster a sense of confidence that can be pivotal in social interactions and self-esteem. Unlike removable dentures, which may shift or cause discomfort, implants provide stability and a natural appearance. This improvement in aesthetics leads many patients to feel more comfortable smiling and engaging with others, thereby positively impacting their social lives.
Additionally, the long-term benefits of dental implants include their durability and ease of maintenance. Unlike other restorative options, implants can last many years, often up to a lifetime, with proper care. They require no special cleaning routines beyond regular oral hygiene practices, making them a practical choice for many. Furthermore, dental implants help preserve the integrity of the jawbone, preventing bone loss that often occurs with missing teeth, which can lead to changes in facial structure over time.
For individuals facing the challenges of tooth loss, dental implants present a viable and advantageous solution. By embracing this innovative treatment, many can restore their chewing function, aesthetics, and confidence, ultimately leading to an improved quality of life. Consulting with a dental professional about the suitability of implants can be the essential first step toward regaining oral health and personal well-being.
In conclusion
dental implants stand as one of the most advanced and effective solutions for restoring natural oral function and improving overall quality of life. They not only bring back a confident smile but also allow patients to chew comfortably and maintain better overall health. With the continuous evolution of dental technology, implants have become a safe, long-term solution that replicates the look and performance of natural teeth with remarkable precision.
Among the leading centers in this field, All-on-X Clinic in Istanbul stands out as a premier destination for patients seeking world-class dental implant treatments. The clinic’s expert team utilizes state-of-the-art digital implant systems and 3D imaging technologies to ensure exceptional precision, functionality, and aesthetics in every case.
Choosing All-on-X means more than restoring your smile — it means reclaiming your confidence, comfort, and quality of life. With comprehensive care and internationally recognized expertise, your journey toward a perfect smile begins and ends in the trusted hands of Turkey’s top dental implant specialists.